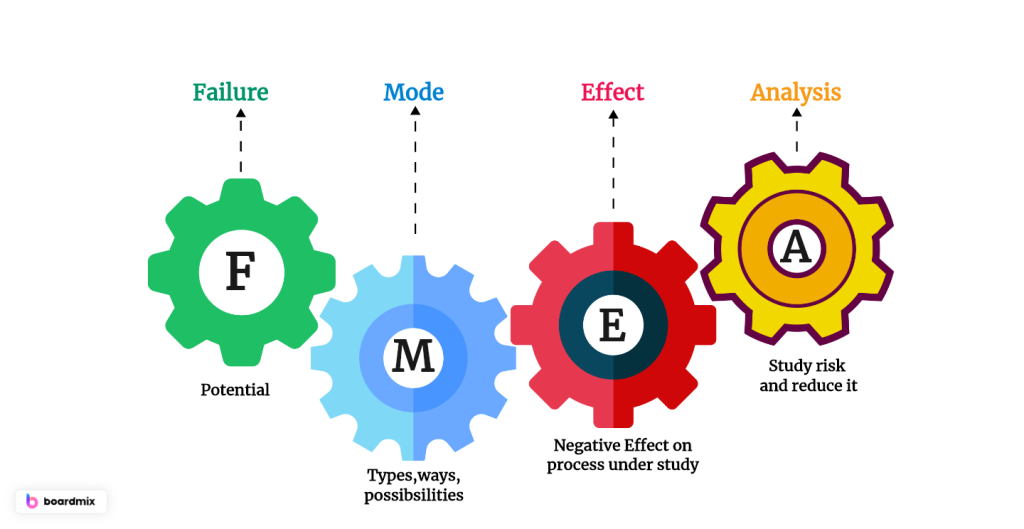
- FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis) is a critical tool in product design to identify and prevent potential failures before production.
- Assigning Risk Priority Numbers (RPN) helps prioritize which failures to address, allowing the design process to move forward efficiently.
- Proper use of FMEA could have prevented a suitcase design flaw that led to a handle breaking, highlighting the importance of thorough pre-production analysis.
Implementing Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) during the design process can save products before they fail. FMEA involves thinking through all the possible ways a product might fail before it goes into production and then updating the design to address those potential failures. By systematically identifying and prioritizing these failures using a Risk Priority Number (RPN), designers can focus on the most critical issues and ensure they are resolved before mass production begins.
RPN is calculated based on the probability of a failure occurring, the severity of the failure’s impact, and the detectability of the failure. By setting a threshold for RPN, design teams can determine which failures must be addressed and which are less critical. This approach helps prevent getting stuck in an endless design loop while mitigating significant risks.
A suitcase example highlights the consequences of not using FMEA effectively: someone who purchased a suitcase had the handle break after two trips. If the company had conducted a proper FMEA, they would likely have identified the weak handle design as a high-risk issue, given its probability of failure, the significant impact on the suitcase’s usability, and the lack of detectability before the handle snapped. Addressing this issue before production could have prevented the negative customer experience and the subsequent poor review. This case underscores the importance of thoroughly analyzing potential product failures to avoid costly and damaging outcomes.


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.