- SaaS security safeguards cloud-based software applications by addressing critical components like data protection, identity and access management (IAM), compliance, endpoint security, and incident response.
- The shared responsibility model highlights that while cloud providers secure infrastructure, customers protect data, applications, and user accounts.
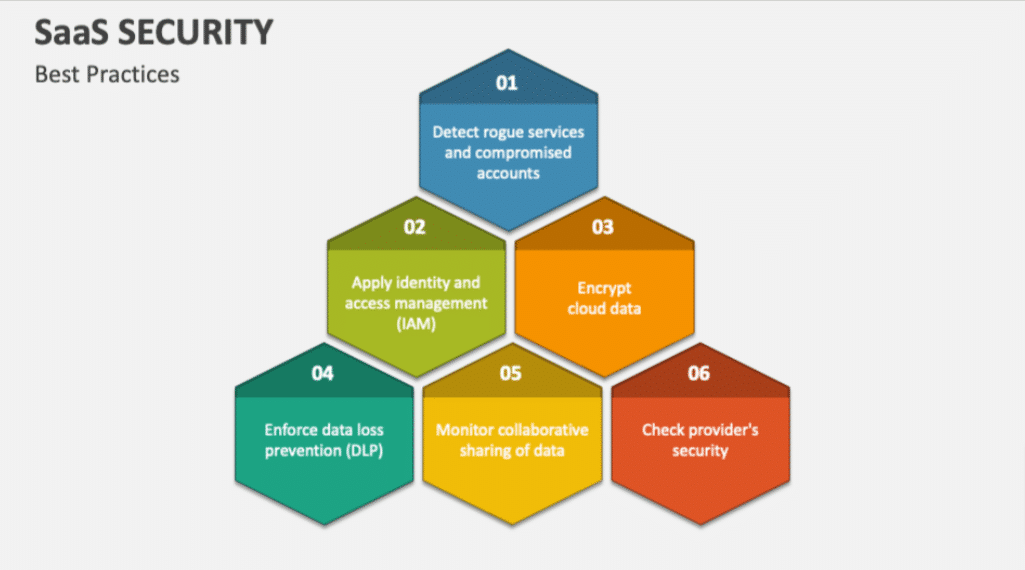
- Implementing a comprehensive SaaS security strategy involves risk assessment, strong access controls, monitoring, compliance alignment, and continuous improvement to address evolving threats.
SaaS security involves securing access to and using cloud-based applications to protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and other cyber threats. It relies on the shared responsibility model, where cloud service providers ensure infrastructure security while customers manage data and application security. Critical elements include encryption, backups, multi-factor authentication (MFA), least privilege access, and regular audits to identify vulnerabilities.
Organizations should emphasize secure configurations, endpoint security, and network protection through tools like VPNs and SIEM systems. Automation and monitoring can streamline processes, detect anomalies, and enforce compliance with frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, or SOC 2. Regular training and awareness programs ensure employees understand evolving threats and their roles in maintaining security.
Best practices for SaaS security include conducting vendor assessments, enforcing role-based access, securing APIs, and establishing incident response plans. Continuous improvement through periodic assessments, updates, and threat intelligence integration ensures businesses remain resilient against emerging threats while maintaining compliance and protecting sensitive data.


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.