- A detailed exploration of integrating Industry 4.0 technologies and principles with quality management methods, specifically through Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), can be presented using a “Smart Factory Line” testbed.
- The case study outlines applying FMEA within the smart factory setting, highlighting the roles and collaboration across different domains of expertise, including quality management, robotics, and cybernetics.
- There are also strategic recommendations for improving FMEA practices and adapting quality management to the digital transformation inherent in Industry 4.0.
A detailed exploration of integrating Industry 4.0 technologies and principles with quality management methods, specifically through Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), can be presented using a “Smart Factory Line” testbed. This method aims to verify the feasibility of applying FMEA in a complex technical system and to demonstrate the potential of integrating Industry 4.0 features, such as automation and digitalization, with traditional quality management techniques. The integration is illustrated in a smart factory environment that embraces advanced manufacturing concepts and technologies, enhancing both product quality and production efficiency.
Applying FMEA within the smart factory setting highlights the roles and collaboration across different domains of expertise, including quality management, robotics, and cybernetics. The structured application of both Design FMEA (DFMEA) and Process FMEA (PFMEA) to various components and processes within the testbed is one application. This approach addresses potential failures and fosters an interdisciplinary understanding and synergy that can enhance the design and operational phases of manufacturing. The findings emphasize the importance of teamwork and integrating comprehensive knowledge bases in executing FMEA effectively in complex systems like those found in Industry 4.0.
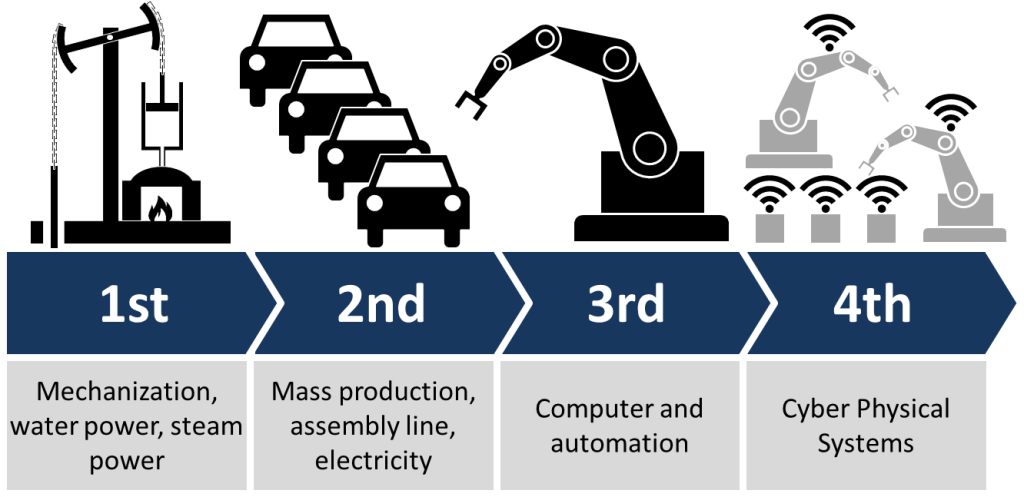
Furthermore, the challenges and opportunities of applying FMEA in an Industry 4.0 environment remain. One issue is the transformative effects of Industry 4.0 on manufacturing paradigms, from mass production to personalized production models that focus on customer-specific requirements. There are also strategic recommendations for improving FMEA practices and adapting quality management to the digital transformation inherent in Industry 4.0. These include enhancing data-driven decision-making, increasing the use of digital twins for process simulation, and further integrating systems to support real-time quality management.


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.