- COBIT is a comprehensive framework for IT governance and management created by the ISACA (Information Systems Audit and Control Association) that ensures the quality, control, and reliability of information systems. It is widely applicable across industries.
- The latest version, COBIT 2019, expands on previous iterations by incorporating six governing principles, enhancing flexibility, and adding new processes to support modern IT operations.
- COBIT audits involve detailed preparation across domains like project management, change management, and asset management, emphasizing evidence-based compliance and stakeholder involvement.
COBIT, short for Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology, is a globally recognized framework created by ISACA to help organizations align IT practices with business goals. It supports IT professionals, compliance auditors, and executives by providing a common language for IT governance. COBIT has evolved significantly since its introduction in 1996, with the most recent version, COBIT 2019, offering enhanced governance principles and objectives to suit modern enterprises.
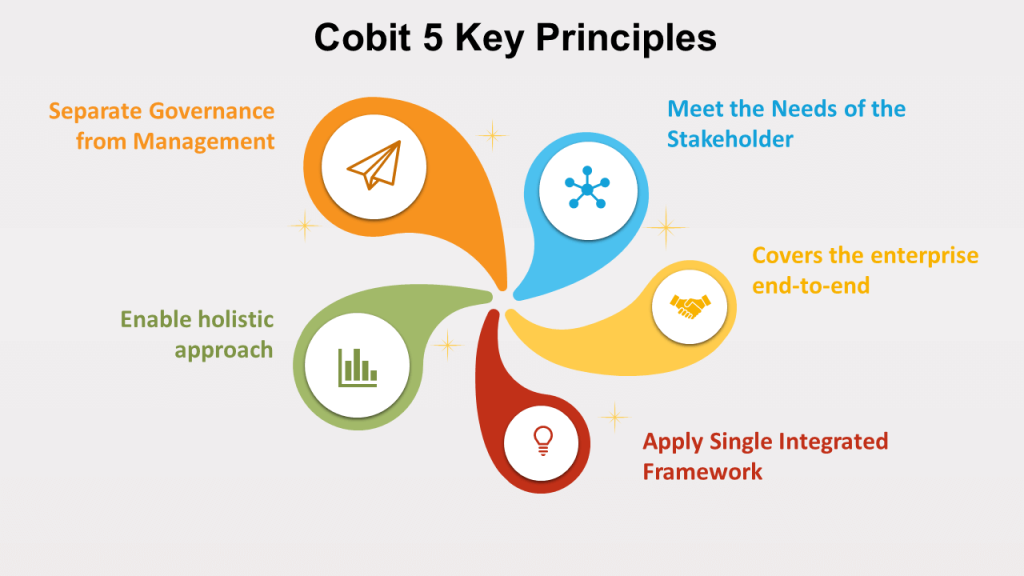
COBIT 2019 incorporates six core principles: meeting stakeholder needs, ensuring a holistic governance system, and tailoring its application to enterprise-specific requirements. This framework enables organizations to manage IT-related risks effectively and align IT processes with business objectives. It emphasizes integrating governance and management practices across various domains, such as planning, monitoring, and supporting IT functions.
Preparing for a COBIT audit requires a systematic approach. Organizations must align IT projects and processes with enterprise strategies, define clear roles and responsibilities, and document compliance efforts meticulously. Auditors often focus on areas like project lifecycle management, configuration changes, and knowledge management. Key criteria include ensuring operational readiness, stakeholder engagement, and risk assessment for IT changes.
The “Build, Acquire, and Implement” phase of COBIT highlights principles like organizational change, managed IT assets, and configuration management. Audits in this domain assess how well systems are designed, tested, and transitioned into operation. Proper documentation, regular reviews, and robust change management processes are crucial for achieving compliance. Ultimately, COBIT offers a structured path for organizations to optimize IT governance and unlock strategic advantages in today’s digital-first world.


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.