- Big Data and Smart Data are pivotal concepts in modern manufacturing. Big Data offers vast, varied, fast data, while Smart Data refines this into actionable insights.
- The transition from Big Data to Smart Data in manufacturing enables enhanced decision-making, increased efficiency, and improved quality control by focusing on relevant and reliable data.
- Smart Data is set to play an increasingly critical role in the future of manufacturing, driving innovations like autonomous production lines, digital twins, and personalized manufacturing.
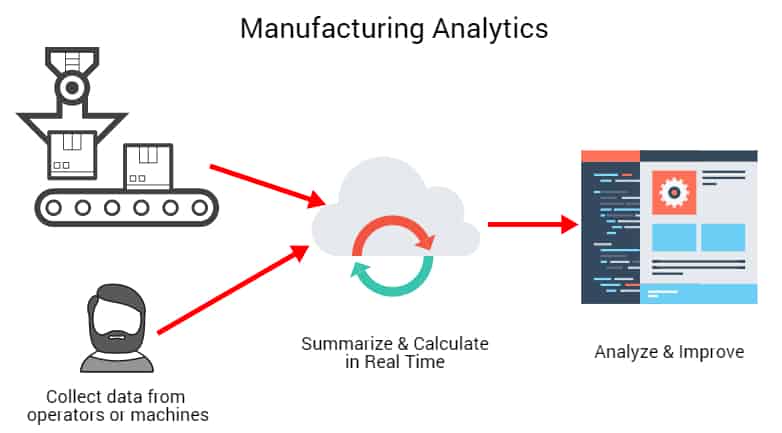
In today’s manufacturing industry, the terms “Big Data” and “Smart Data” are fundamental to understanding the evolution of process control. Big Data refers to the enormous volumes of data generated at high speeds from various sources, such as machines, sensors, and supply chain systems. This data, characterized by its volume, velocity, variety, and veracity, provides a comprehensive view of the manufacturing process but can be challenging to manage and interpret effectively.
On the other hand, smart data is a refined subset of big data focused on quality rather than quantity. Smart Data is relevant, actionable, accurate, and contextually rich, making it crucial for effective decision-making in manufacturing. While Big Data lays the groundwork by providing a broad view, Smart Data distills this information into essential insights that directly impact process control, improving efficiency and quality.
The transition from Big Data to Smart Data is transformative for manufacturing. Smart Data enhances real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and quality management by providing detailed, actionable insights that streamline operations and ensure higher product quality. As the industry continues to evolve with advancements in AI, machine learning, and IoT, harnessing Smart Data will be vital for achieving competitive advantage and operational excellence, ultimately driving the future of data-driven manufacturing.


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.